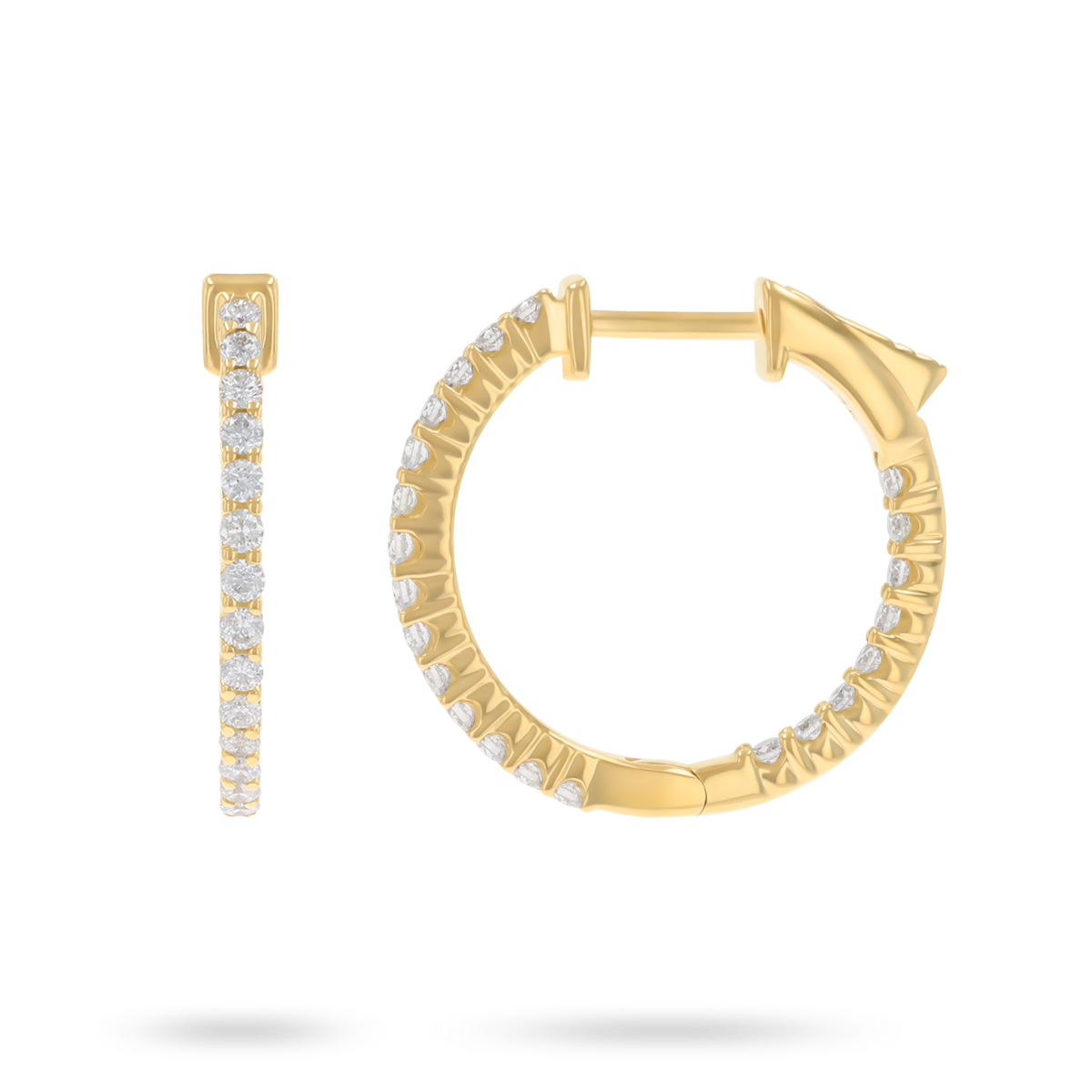The Spectrum of Colour
What is a Diamond?
Diamonds, are composed of carbon and can come in a rainbow of colours from: colourless, yellow, orange, red, pink, purple, violet, blue, green, brown, grey and black. The gemstone is transparent and reflects an adamantine lustre. Moreover, diamonds possess the magical phenomenon of fire, which relies on the facetted gemstones ability to disperse (split) light into its spectral colours.

18ct Yellow & White Gold Pear Shaped Fancy Yellow Diamond Double Halo Pendant & Chain
Crystal Habit
The gemstone crystallises with an octahedron form, exhibiting eight triangular shaped faces or a dodecahedron form, displaying twelve rhombus shaped faces and is classified under the cubic crystal system. The surface of the octahedral crystal, displays triangular etch pits, known as ‘trigons’, whereas the surface of the dodecahedral crystal, showcases grain lines along the length of the rhombic face, always 90° to the adjacent faces. Both forms exhibit curved crystal faces, with rounded edges, as a result of physical tumbling in the magma. Alternatively, diamonds can be found as macles, which are twinned octahedral crystals, essentially one half of the octahedron is in a rotated position, forming a triangular shape. Macles also have trigon markings and grain lines, as well as herringbone markings, a naat and a re-entrant angle. Diamonds rarely occur as cube (six square faces) or icositetrahedron (twenty-four pentagon shaped faces) forms.

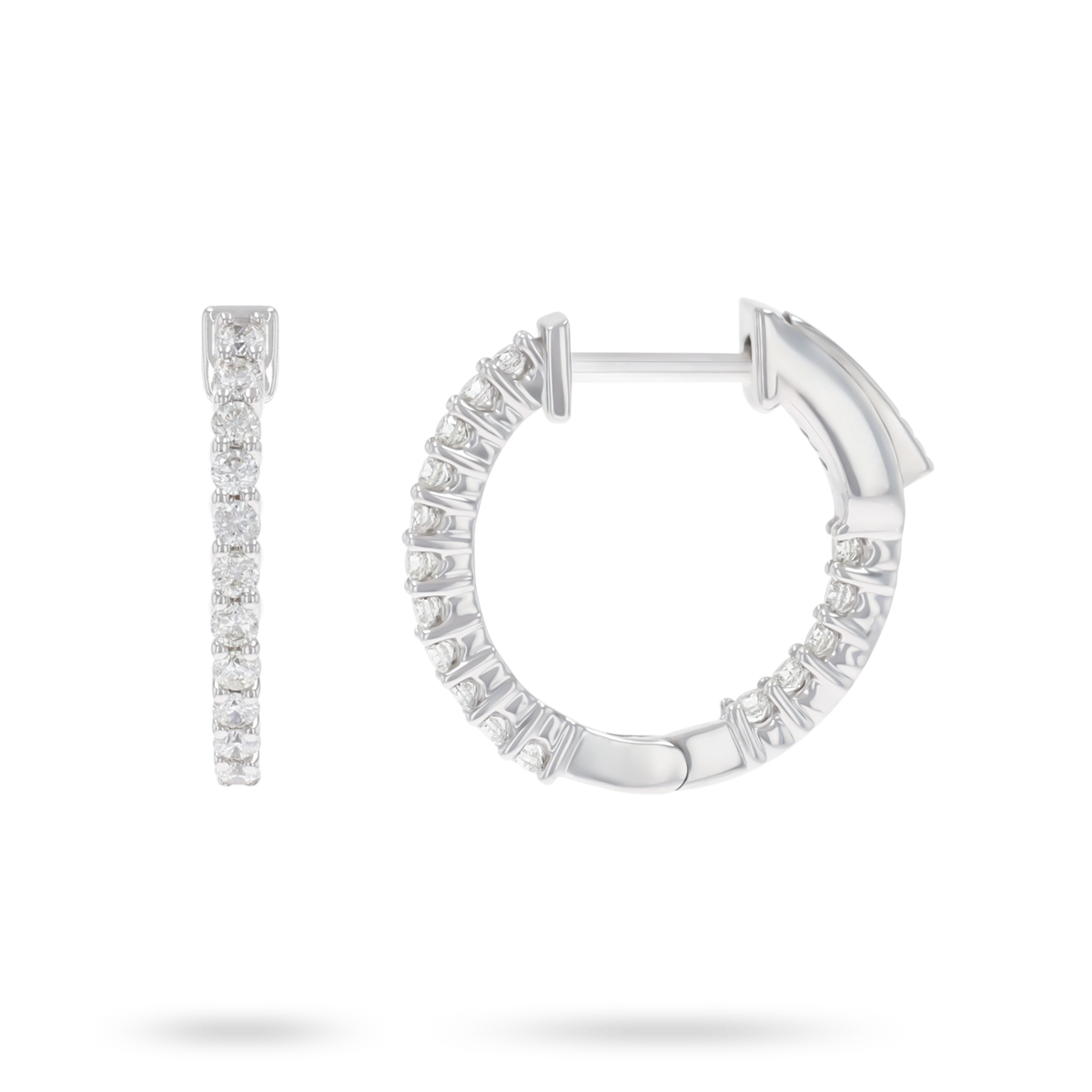
9ct Yellow Gold 0.50cts Diamond Hoop Earrings & 9ct White Gold 0.33cts Diamond Hoop Earrings
Timeline & Localities of Diamonds
Diamonds were first located from a secondary, alluvial deposits, uncovered near the Golconda region in India, 800 BC. Small quantities of alluvial deposits were later found in Indonesia (Borneo), in the 10th century. In 1725, larger quantities of alluvial deposits were discovered in Minas Gerais, Brazil. The first primary deposit of diamonds, was unearthed in South Africa, in 1867 and catalysed the diamond rush, providing a reliable source, that recovered diamonds in a vast range of sizes and qualities. Since then, other primary deposits for diamonds were further detected in: Russia 1954, Australia 1978 and Canada 1990. It is worth noting, that an influx of pink diamonds was an important locality, sourced from the Argyle mine in Australia, which has recently ceased mining in 2020 (during activity, it contributed to 90% of the word’s pink diamond supply).

9ct Yellow Gold Diamond Tennis Flexible Bangle & 9ct White Gold Diamond Tennis Flexible Bangle
Under The Loupe: Inclusions
Diamonds, have a multitude of mineral inclusions from: olivine, garnet, pyroxene, spinel, diamond (yes although a rare occurrence, a diamond can crystallise around another diamond), chromite and magnetite crystals. Additionally, diamonds can display grain lines, gas clouds, feather-like inclusions and cleavages. As well as internal characteristics, diamonds have external characteristic that can be observed, such as: sharp facet edges, naturals on the girdle (trigon markings left from the rough crystal), v-shaped nicks on girdle and bearding (seen near the girdle).

18ct Yellow & White Gold Diamond Bezel Set Bar Link Collarette Necklace
Treatments
Diamonds can be treated to either improve their colour or clarity. Unlike other gemstones, any treatment applied to a diamond, must be properly disclosed before purchase. A diamonds clarity can be improved, with application of laser drilling, which permanently reduces the appearance of dark mineral inclusions. Or, through the use of fracture filling, a non-permanent treatment, that visually reduces the appearance of surface reaching fractures or cleavages. A diamonds colour, can be improved with application of HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) treatment, where natural brown diamonds permanently change colour to colourless, yellowish green, pink and rarely blue. On the other hand, natural yellow to brown diamonds can be irradiated to produce blue, bluish-green, green and black diamonds. Afterwards, these diamonds can be annealed to orange, yellow, brown and pink. Irradiation is a non-permanent treatment and the colour will fade, if exposed to strong light over time. Additionally, diamonds can be further treated by dyeing, coating and foiling.

Synthesis & Simulants
Diamonds can be synthesised via two methods: HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) and CVD (Chemical Vapour Deposition). It is important to acknowledge, that synthetic diamonds are significantly cheaper than natural diamonds. However, the synthesis of diamonds are far more costly, than the synthesis of any other gemstone (for example synthetic sapphire), as the conditions required to replicate a diamonds formation, uses more expensive technology and machinery.
Diamonds can often be mistaken for cubic zirconia, synthetic moissanite, synthetic sapphire, synthetic spinel and artificial glass. These can all be identified through the use of gemological testing and observations.

9ct Yellow 1.00ct Diamond Tennis Illusion Set Bracelet & 9ct White Gold 1.00ct Diamond Tennis Illusion Set Bracelet
The Lore of Diamonds
Diamond is the material used to celebrate the 10th and 60th wedding anniversary, as well as being the birthstone of April, it is also the zodiac birthstone of Aries. Diamond, derives from the Greek word ‘adamas’, which translates to ‘invincible’. Today, the meaning somewhat refers, to the gemstones excellent hardness (ranking 10 on Mohs' scale), hence diamonds are highly resistant to be scratched or abraded by another material, other than diamonds itself.
The ancient Egyptians thought diamonds symbolised life, and the Pharaohs were known to place the gemstone in the centre of an ankh cross. Whereas, the ancient Greeks believed diamonds to be the tears of the gods or broken splinters from fallen stars. Alternatively, in ancient Roman literature it is noted that Cupids arrows were ‘diamond tipped’, maybe one of the first references that associates the gemstone with love.

Oval Signet Ring With Diamond Bezel
Care
Diamond: 💎 Hardness: 10 | 💪 Toughness: Good | ⚖️ Stability: Excellent
💚 Low Caution: A very durable gemstone, generally it is safe to use in; 🫧 Jewellery Dips, 🔊 Ultrasonic, 🌪 Steam Cleaners.
🔬Gemmological Observation: Diamonds have excellent hardness, this means only a diamond can scratch/abrade another diamond. To avoid scratches, store your diamond set jewellery separately. Diamonds only have good toughness, as they possess perfect cleavage. This means that if knocked in the wrong direction, the diamond can cleave/fracture. Whilst wearing, you will need to ⚠️ avoid: 🔨 Sharp Knocks. If the diamond is heavily fractured, you will need to ⚠️ avoid using: 🔊 Ultrasonic, 🌪 Steam Cleaners.

Explore our Wordfinder, A Glossary of Terms, to discover the meaning behind unknown names, terms or phrases - used in this article.













 Contact Us
Contact Us