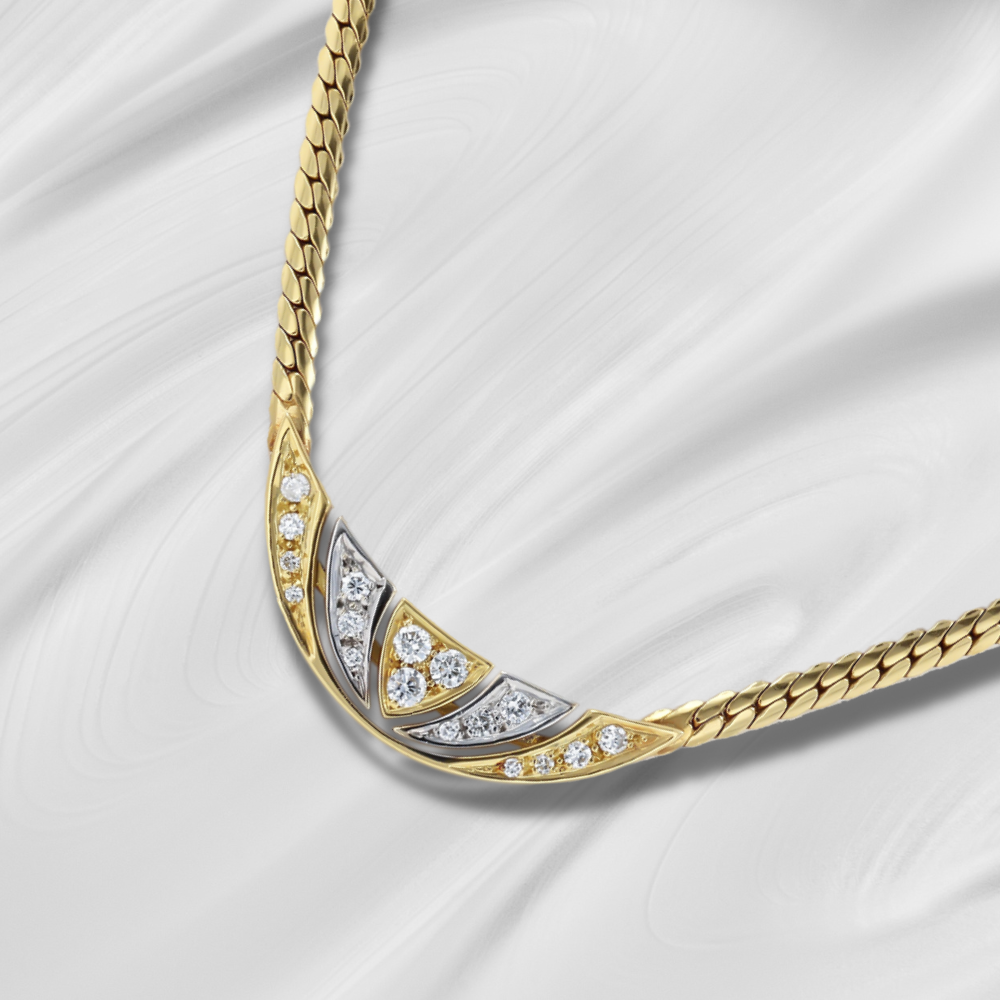
These hoop earrings are crafted in 9ct rose and white gold, featuring a tube profile with an oval silhouette. The earrings are complimented with a v-clip fitting.
Evolution of jewellery manufacturing, means that earrings are no longer filled with wax, or are too heavy to wear (splitting earlobes). With development and advanced within the industry, they are designed to be comfortable, lightweight and made to last.
Jewellery Odyssey:
Throughout the history of jewellery, earrings have been worn across many ancient civilisations and cultures, by both women and men. Archeologists have discovered that over 5,000 years ago, the ancient Sumerians would often import gold or silver (from modern day Iran and Turkey) along with lapis lazuli (Afghanistan) and carnelian (India), to embellish their intricate jewellery designs. During this era it was fashionable for both men and women to wear earrings.
Located on the Greek Island of Crete, the beautiful, colourful and expressive Aegean culture, thrived during the Bronze Age Greece (c. 3100 BCE - c. 1100 BCE). Minoan women used fashion, hair and jewellery such as hoop earrings, for a decorative and bold statement.
From being commonly worn by Ancient Egyptian children, to the upper classes of the Roman Empire, earrings continued to remain a favourable accessory. During the renaissance epoch, smaller earrings including baroque pearls, were famously seen being worn by both men and women. The ornate, opulent and chandelier design of Girandole earrings, during the Georgian period, were extravagantly heavy. In contrast, single stone solitaire earrings rose to prominence, towards the end of the Victorian era.
Within the last 100 years, the design of earrings have been influenced by art nouveau, art deco, retro, modern and contemporary periods. Culminating in a diverse range of earrings styles with multiple piercing options. It has never been more exciting to curate your earring style!
Jewellery Care Precautions:
Avoid direct contact with: perfume, lotions, skincare, hairspray / other chemicals. Remove, your jewellery: when showering, swimming (as both chlorine and saltwater will react with metals), washing your hands / using hand sanitisers, before going to bed or when participating in physical activities (going to the gym, exercising, gardening, housework etc….).
Beware, metals may tarnish over time due to oxygen contact and natural body oils. Prevent items from being exposed to moisture and direct sunlight, for long periods. Store jewellery in a dry place away from humidity, in a pouch/jewellery box and keep each piece separated from each other. Care, for your jewellery by cleaning with a soft dry cloth.
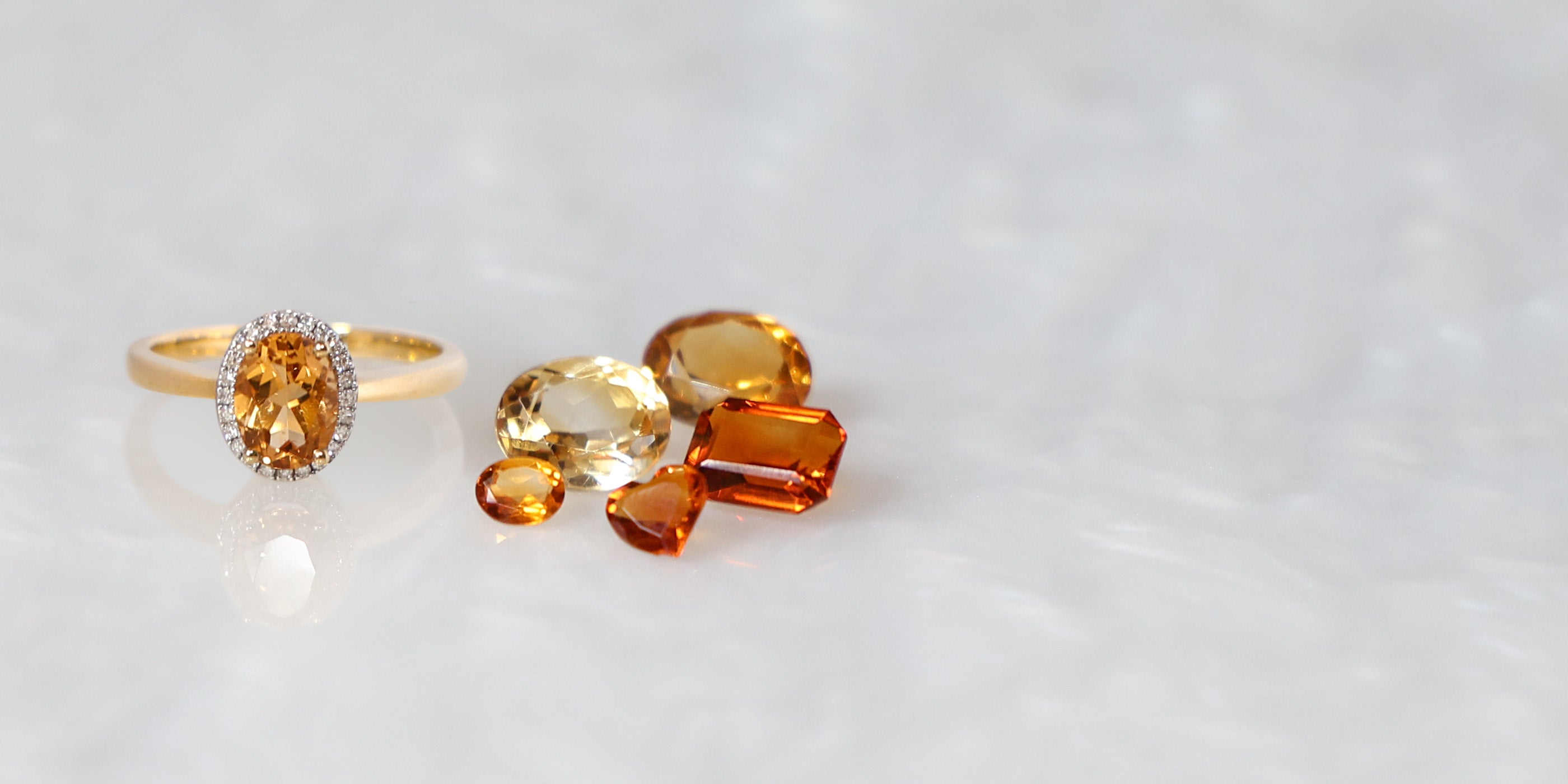
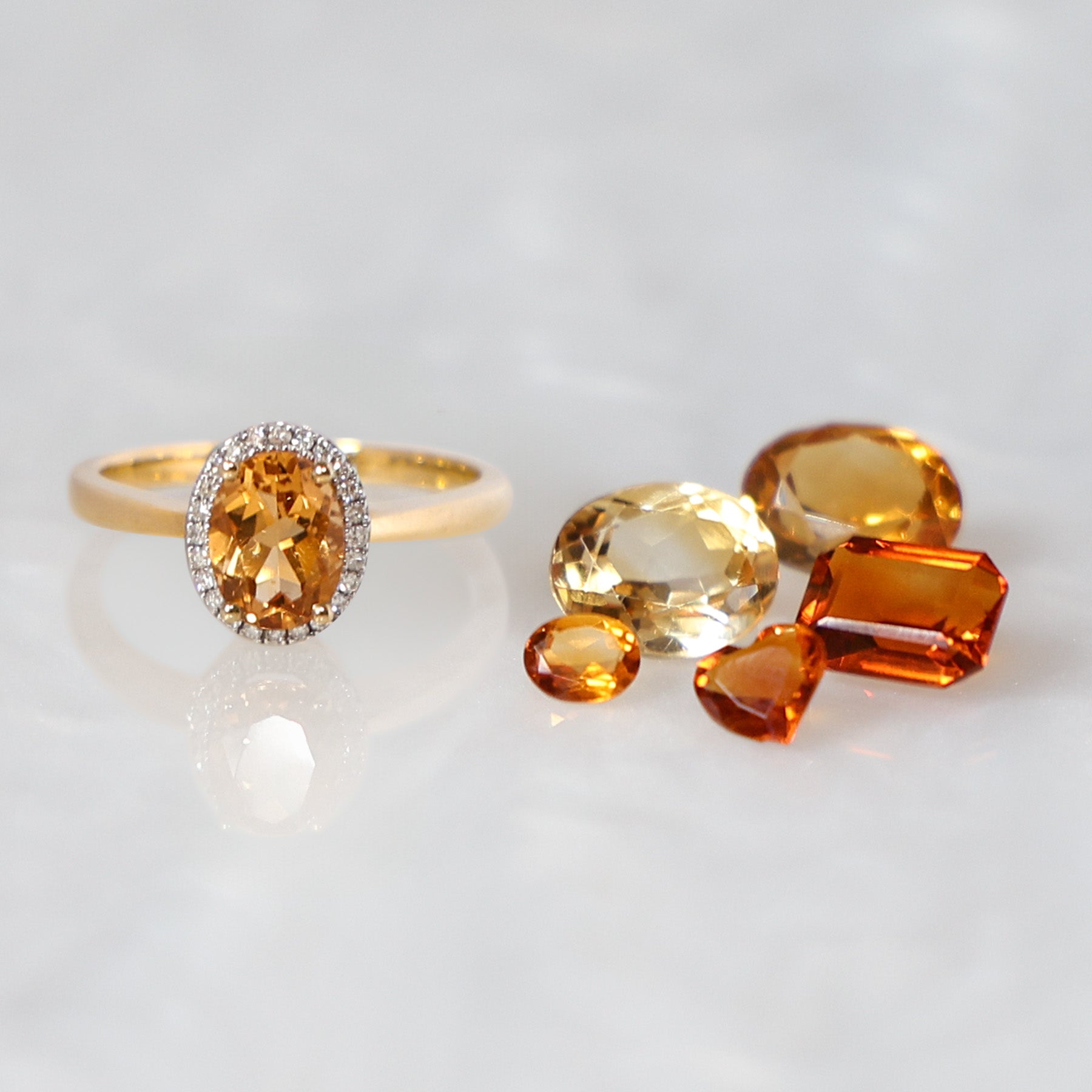
Rose Gold:
Rose gold is not an element and does not occur naturally in a pure form. Pure yellow gold is mixed with alloys of copper and sometimes silver to produce, a reddish pink coloured alloy, known as rose gold. The colour and depth of rose gold will vary, depending on the ratio of yellow gold to copper. The lower the carat of yellow gold, the higher the copper content, the deeper the colour. The colour of 9ct rose gold will be a deeper reddish-pink, 14ct rose gold will have a subtle rosy pink colour and 18ct rose gold, will show a soft champagne pink colour with a yellow undertone.
Over time and especially in humid conditions, the copper alloy naturally oxidises with the air, causing rose gold jewellery to develop a deeper reddish patina. Seen frequently in antique rose gold jewellery, this patina takes years to develop and adds a desirable vintage essence to the jewellery.
Whilst rose gold jewellery will not discolour easily, it is important to avoid exposure to household chemicals, bleaches, toothpaste, baking soda and other cleaning abrasives. Wearing jewellery in places where perfumes, hairsprays, body lotions have been applied on your body, will increase tarnishing. Wear your jewellery after the products have been applied. To clean your rose gold jewellery, use a mild soap with warm water and dry with a soft cloth. For professional cleaning, our workshop can polish your jewellery back to life.
White Gold:
White gold is not an element and does not occur naturally in a pure form. Pure yellow gold is mixed with alloys of white metals (such as palladium) to produce, a silver coloured alloy, known as white gold. It is further coated in a precious metal called rhodium (an element that derives from the same metal family as platinum), to increase its lustrous sheen and protect it from tarnishing and scratching.
Over time with exposure to oxygen and moisture, the rhodium coating will naturally wear and you will begin to see the natural yellow colour of gold. Rings will experience this more than other types of jewellery. The general guide for re-applying rhodium coating to your rings is between 1-2 years. However, the rate of wear depends on the pH level of your skin, exposure and contact to chemicals. For professional cleaning and rhodium coating, our workshop will provide the TLC your jewellery needs.

















 Contact Us
Contact Us